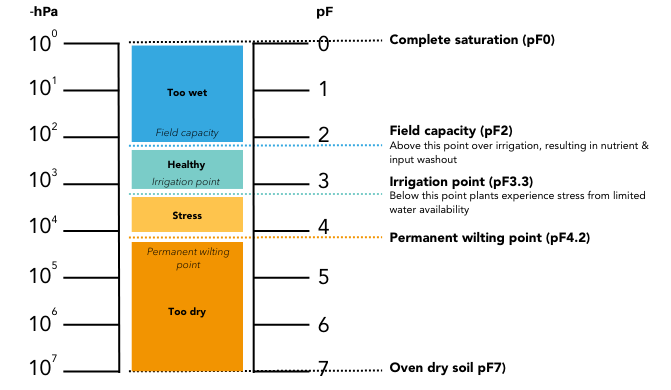
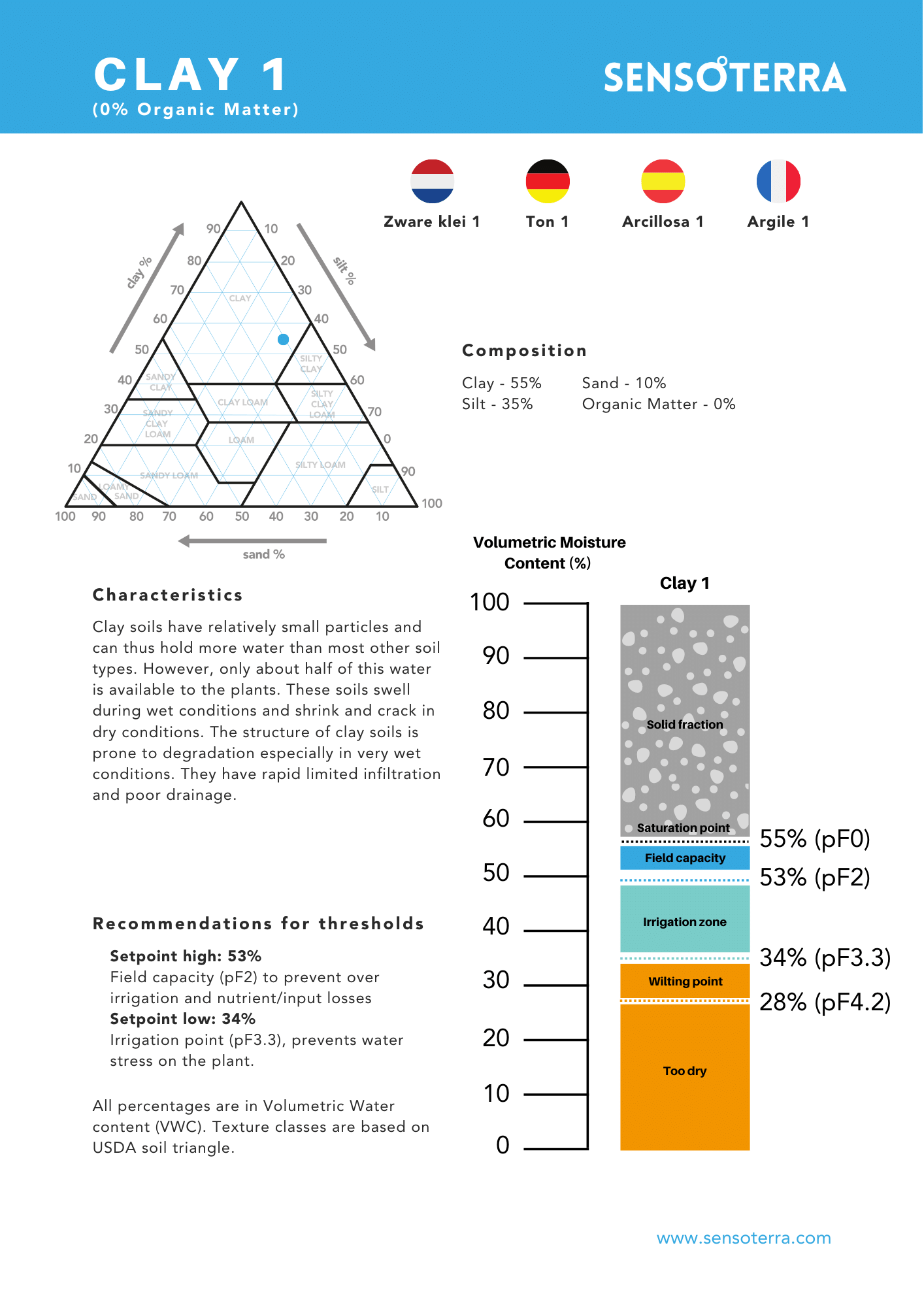
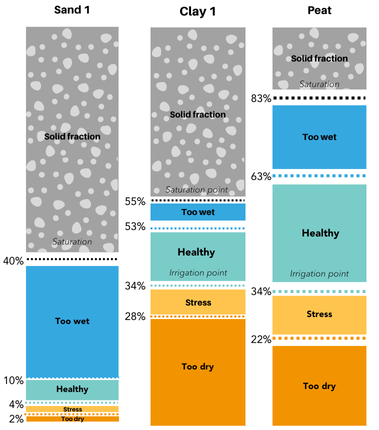
Different soil types have different ‘soil moisture behavior’. Every soil type has an ‘ideal’ window (percentage range) of soil moisture – which is called ‘plant available water’. At the low end, plants will wilt. At the high end (field capacity), nutrients will wash out and less air will be available for the roots. Not many people know that these windows can vary greatly, based on variations in size of the pores in the different soils. This is why calibration is so important.
The Sensoterra sensors work in all soil types. However, the right calibration is crucial for improving the accuracy and precision of the soil moisture measurements. Sensoterra has its own laboratory, based in Utrecht, where soils are analyzed to add new calibration curves to continuously improve soil moisture accuracy.
We’ve put together this reader to support your decisions on selecting the correct soil type by sensor.